Rover Perseverance and Harmonic Drive® discover Mars
As part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program, Rover Perseverance faces a major challenge: to explore the Martian rocks and climate of the red planet. To do this, it uses a robotic arm equipped with Harmonic Drive® Gears.
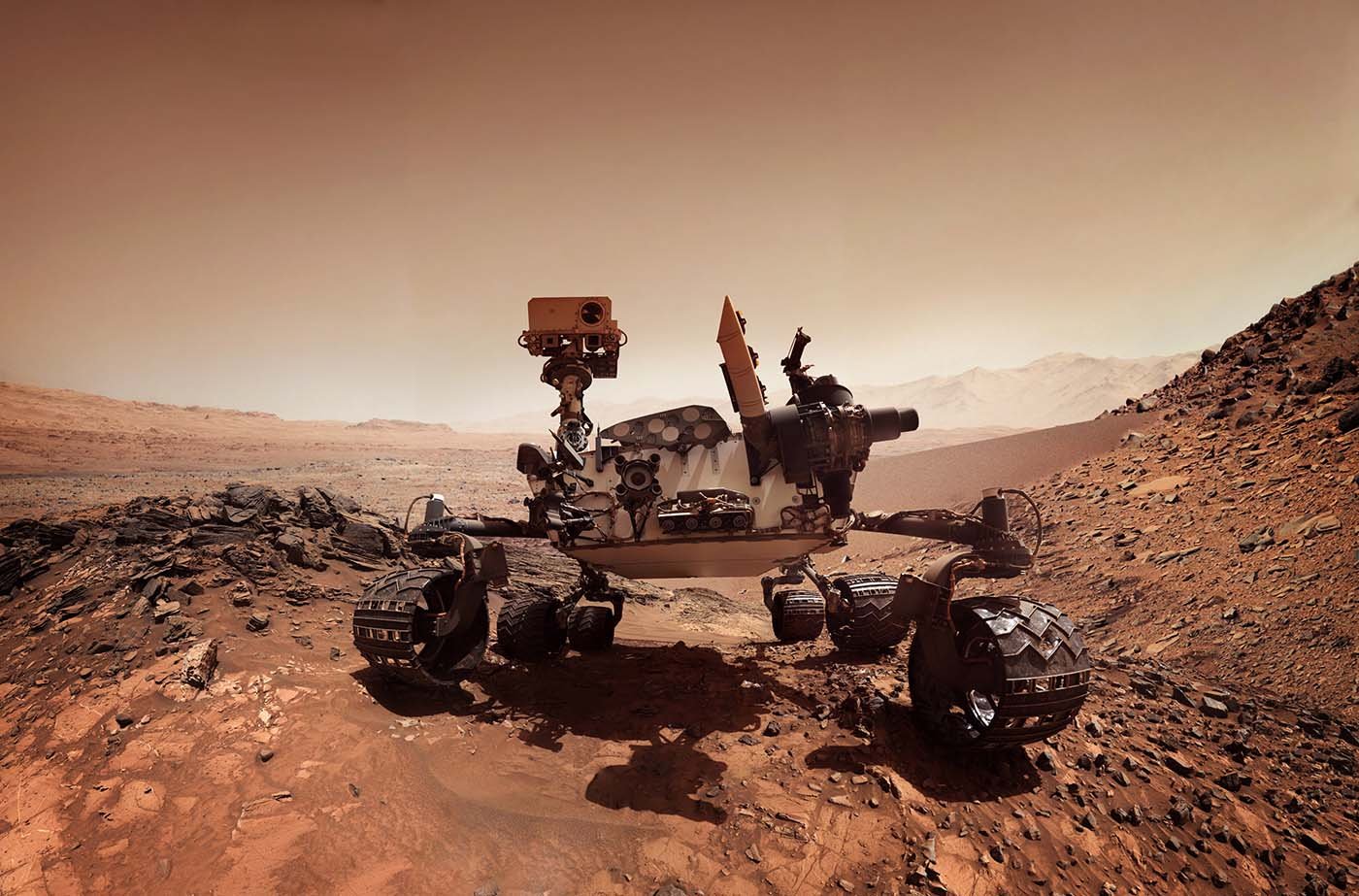

The Red Planet
Millions and millions of kilometres separate it from Earth: In earlier cultures, Mars was considered threatening and aggressive because of its colour. According to today's knowledge, this cannot be completely dismissed. It is cold on the red planet, while dust storms pass over it at speeds of up to 400 km/h. Right in the middle of things – Rover Perseverance and Harmonic Drive® Gears.
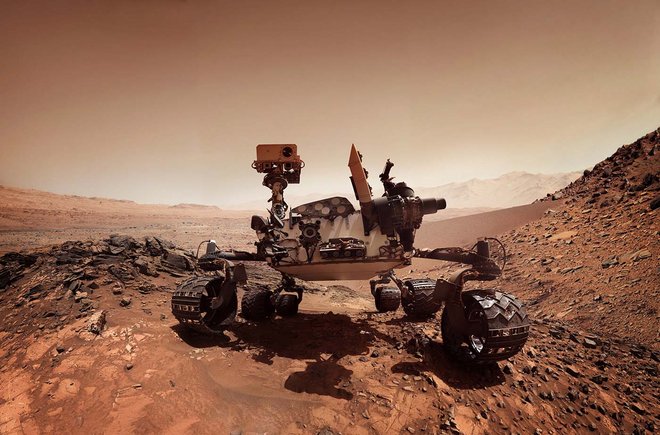




Mission explores life on Mars
The mission's objectives are in line with those of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Four tasks for Perseverance's Mars mission are clearly defined and take place within the framework of scientific research. These are:
- Determine if life ever existed on Mars: the rover will search for preserved signs of life, called biosignatures, in an area of Mars that may have been favourable for life in the past.
- Characterising the Martian climate: with its dedicated instruments, Perseverance will study the climate conditions on Mars and find signs that the planet was once habitable and may be in the future. In doing so, it will also work with the research results of the rover Curiosity.
- Characterising Mars geology: Perseverance collects rock samples, seals and stores them both inside itself, and on the Martian surface. These samples could be recovered on future Mars missions and sent back to Earth for more in-depth study.
- Preparing for humans: The rover provides experimental technology that attempts to extract oxygen from the Martian atmosphere. This capability could pave the way for future manned missions to Mars.
The mission itself personifies the human ideal of persevering toward the future and will help us prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
Robotic arm replaces human geologists
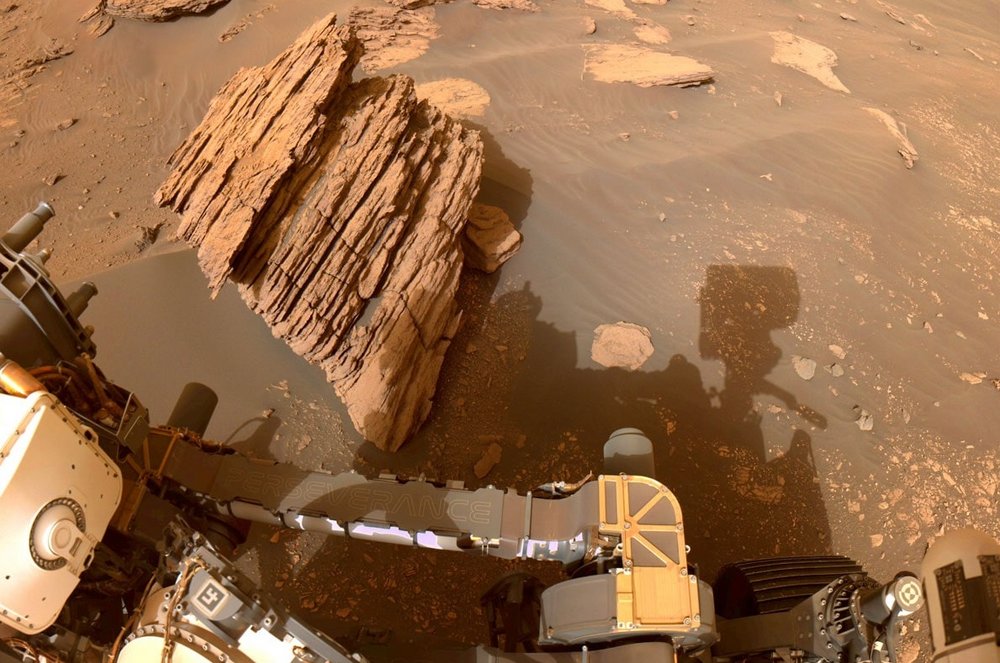
In order to be able to fulfil the various research objectives of the mission, Rover Perseverance is equipped with a robotic arm measuring over 2 metres. Its functionality and freedom of movement resemble a human arm in many respects. It has 5 degrees of freedom, or actuators, which are modelled on the human shoulder, elbow and wrist joints. The intention of this structure is to replicate the work of a human geologist as closely as possible. At the end of the robotic arm, the hand, Perseverance is equipped with several scientific tools. Instruments installed on the turret include a stereoscopic imaging system, spectrometer, ground penetrating radar and sensors. The rover is able to take rock cores using a percussion drill, take microscopic images and analyse the elemental and mineral composition of rocks and soil on Mars.
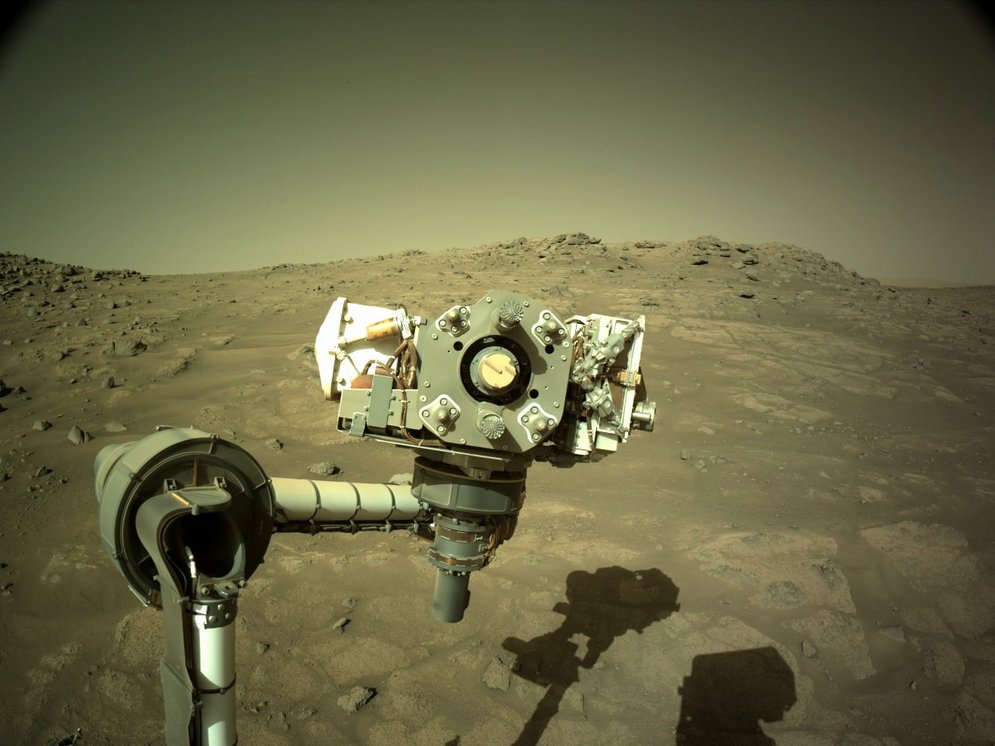
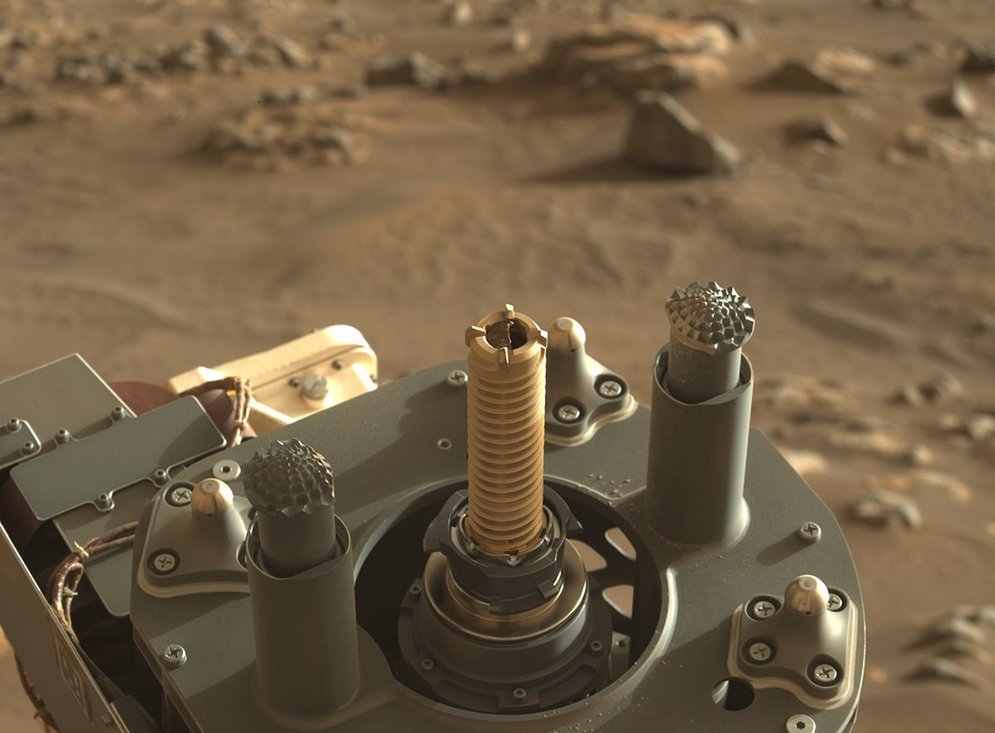
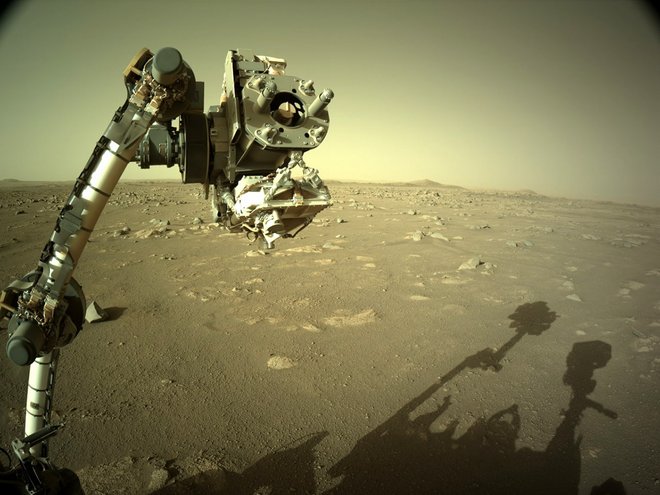






Great freedom of movement thanks to five Harmonic Drive® Gears
The freedom of movement and functionality of the robot arm are fundamentally based on the drive elements installed in its joints. No less than five Harmonic Drive® Gears are integrated here and enable reliable, precise and backlash-free positioning for the perfect execution of scientific work.
- For horizontal and vertical movement, the rover's shoulder joint has two drive units. Whilst in the horizontal plane a freedom of movement of 160° is made possible, in the vertical plane it is 70°.
- The actual arm is guided by another drive element, moves 290° and can be extended both upwards and outwards.
- The wrist responsible for positioning the turret and thus the tools is equipped with two drive units that allow vertical and horizontal rotation through 340° and 350°.
Did you know?
Perseverance was scheduled to spend at least one Martian year on the red planet - the equivalent of about 687 days on Earth. The rover has long since broken this milestone.
Landing in the Jezero Crater
A terrain that is exciting for scientists can be challenging not only during landing, but also in general for the rover's system components. Nevertheless, Perseverance managed to navigate to the chosen landing site on the planet, avoid the dangers of landing on its own and manoeuvre successfully to date. Welcome to the Jezero Crater!
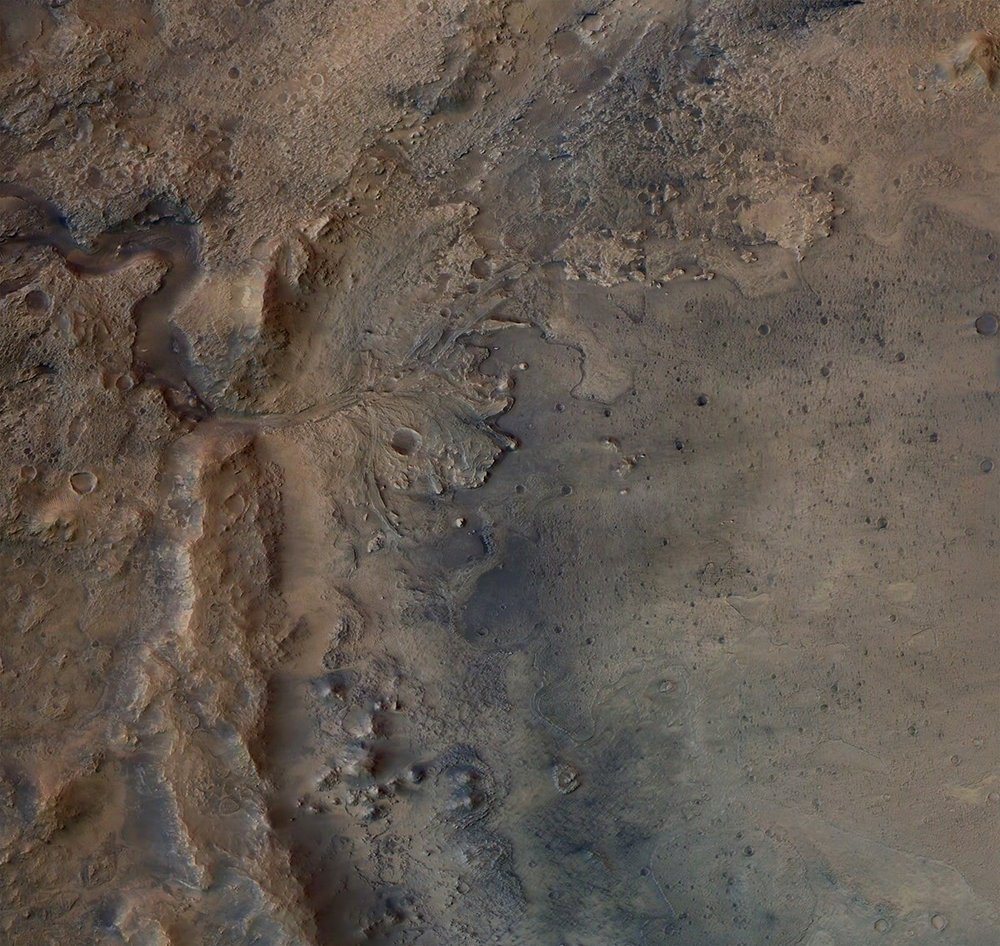

Former river delta fascinates
Members of the mission team and scientists from all over the world were involved in selecting the landing site. More than 60 sites on Mars were carefully studied before Jezero Crater was chosen. The 45-kilometre-wide basin is characterised by a fascinating ancient river delta with steep cliffs, sand dunes and boulder fields. Around 3.5 billion years ago, a river is said to have flowed here into a body of water the size of Andorra. Today, the crater is completely dry, but offers high potential for research and possibly the discovery of microbial life. (Picture: ESA/DLR/FU-Berlin)
A milestone in space exploration
With humanity's first sample collection on another planet, Perseverance documented a milestone in the history of space exploration. But its mission is not yet over. Mars Rover Perseverance and the integrated Harmonic Drive® Gears in a quick check:
-
0Precision gears
-
0Days+ on Mars
-
0Martian kilometres
Emre Dinler
Senior Manager Aviation & Space
Your contact
Tel: +49 6431 5008-760
Email: emre.dinler@harmonicdrive.de
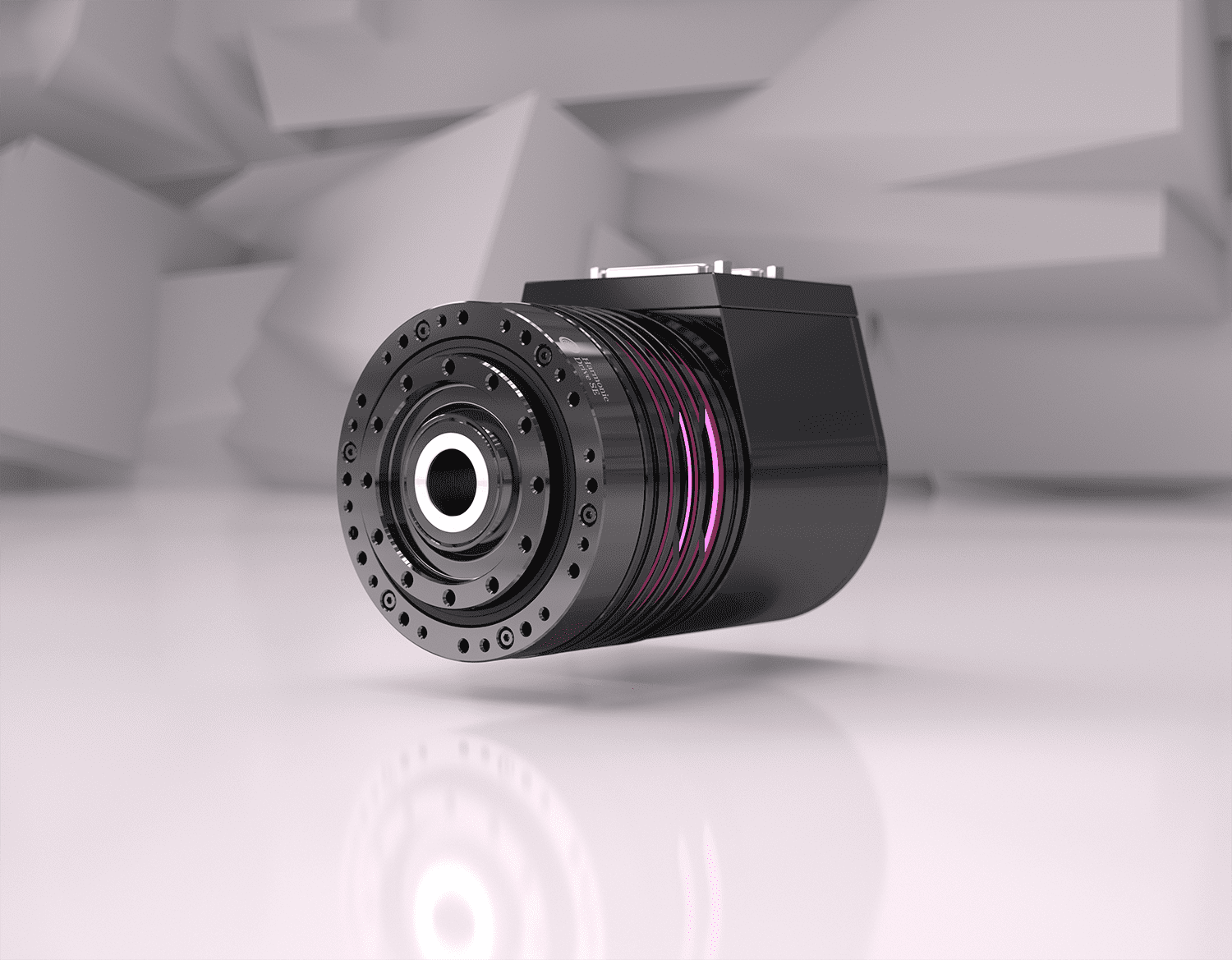
Smart System IHD: Pioneering drive technology
The need for compactness and intelligence is growing, especially in industrial and mobile drive technology.
View
Core competence design & development
Highest quality is created with passion. A passion that is realised through deep technical expertise and state-of-the-art processes.
View
Around the globe with the ISS – Research at 400 kilometres altitude
In these applications on the International Space Station, Harmonic Drive® products ensure reliable operation.
ViewNote: Certain or all of the graphics depicted on this subpage originate from NASA archives or services. Copyright belongs to named agency.

